By Lale Lovell, PhD, Vice President for Transformance Advisors
Valuable Tool
Everyone wants to delight the customer, but what does that really mean? One valuable concept to help you systematically figure out how to delight customers is called: Critical to Quality (CTQ). These are key attributes of a product or service which customers have defined as being important.
CTQ is also a process which allows you to take a customer’s need and drill down to specify requirements from the customers perspective. You can then quantify your ability to fulfill those needs. If done properly, leveraging Critical to Quality will lead to a high-quality customer experience.
The key elements of Critical to Quality are called Needs, Drivers, and Requirements. They are identified, determined, or specified and placed into a “tree” shaped diagram called a Critical to Quality Tree (CTQ Tree). One starts with a customer’s need, determines the drivers of that need, and then specifies the requirements (standards or performance measures) of those drivers.
A CTQ Tree is applicable whether the customer is internal or external. You can view the next department in a process as an internal customer. Alternatively, the person or organization buying your products or services is an external customer. Furthermore, investors, regulators, special interest groups, and all sorts of other stakeholders can be viewed as external customers.
While CTQ Trees sound straightforward, a key to making them successful is to start down the right path by truly understanding your customer’s needs. Let’s look closer at the systematic steps for creating a CTQ Tree.

“Critical to Quality (CTQ) are key attributes of a product or service which customers have specified as being important.”
1. Identify Needs
What is meant by a customer needs analysis? A need is: “something which your product or service must deliver for customers to be happy”. How can you identify these needs? In a simple example, a customer may need to go out for dinner. In another situation, a customer may need their roof repaired.
Understanding customer needs can be a guessing game, especially if you do it in a silo with no input from the customer. Luckily, many methodologies exist to help you truly understand the Voice of the Customer (VOC). All of them rely on you taking a look at your product or service from the customers point of view. Surveys, interviews, focus groups, observations, complaints, customer journey maps, and social media postings are some of the popular choices. One must be careful to ensure that you construct these data gathering techniques to be unbiased and focused on the customer. Many resources exist to help one gather strong VOC data, from lists of good interview questions to software packages that can gather direct information on the user experience.
After collecting VOC data, you need to identify themes reflecting your actual customer needs. An affinity diagram is one visual tool you could use for theme identification. These themes are then prioritized to determine the top “needs” of your customers. This is a critical step to ensure you are starting the CTQ Tree with a strong trunk. You don’t want the exercise to be viewed as garbage in, garbage out.
A CTQ Tree will be built for each customer need. Three themes, or needs, will require you to build (or grow) three trees.

“Voice of the Customer (VOC) is a method for understanding customer needs and expectations.”
2. Determine Drivers
A driver is: “something customers will use to evaluate the quality of your product or service”. In our simple example, a customer seeking to go out for dinner may view the quality of food and drink as a driver in their selection of where to go.
Taking your customer needs, you will determine what drivers will help fulfill each need. These drivers will be be the first branches of your tree. The idea is to break down the generic concept of the need into a more specific element that the customer will consider critical to their experience with your product or service. Thus, drivers are more specific attributes the customer will use to evaluate the quality of your product or service. Typically, there are three to five drivers for each need.

3. Specify Requirements
A requirement is: “the measurable performance, which must be met, in order to provide a high-quality product or service to your customers”. In our simple example, a customer seeking to go out for dinner may specify selection and price as measurable attributes for the quality of food and drink.
Requirements should be quite specific and measurable in some way. These requirements will be the outer branches of your tree. Ideally, each driver will have two to three requirements which are critical to the quality of your product or service.
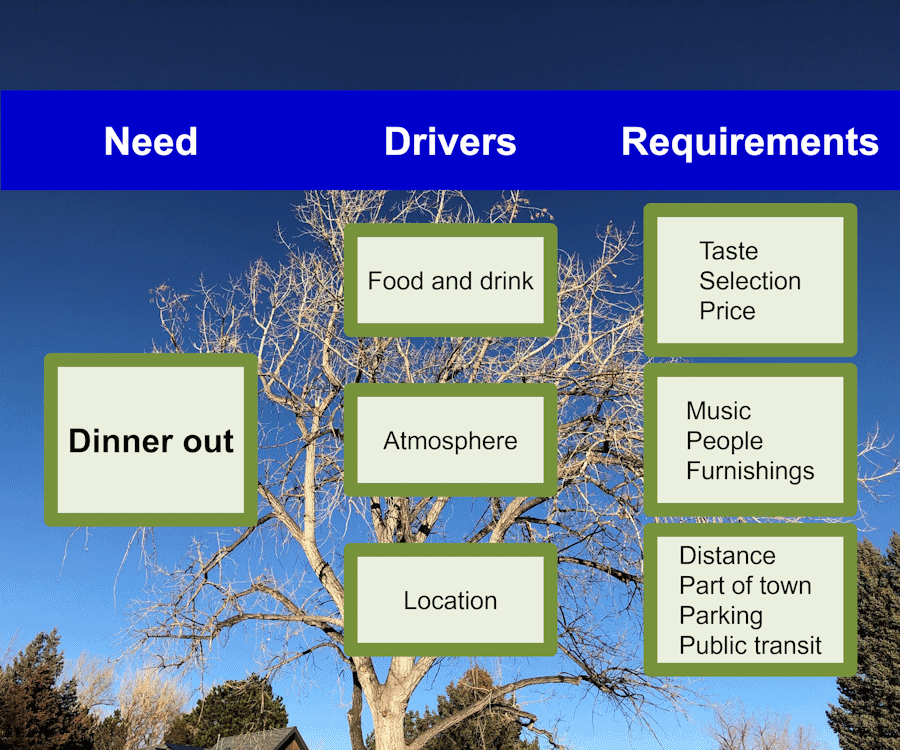
Example 1
Let’s work our simple example and make a CTQ Tree. The scenario is “you are traveling to a new city and have to go out for dinner”. Dinner out is your need. You would list “dinner out” on the left side of the page.
Next, ask yourself: “What drivers are important considerations for your need?” What is really needed to have a great dining experience? Thinking about your need, you might list your top priorities as food and drink, the atmosphere of the dining room, and the location of the restaurant. Those three things are your key drivers and would go as the first branches of the tree.
From there, think about each of your key drivers. It’s time to specify the measurable performance, which must be met, in order to met your quality expectations. For example, for food and drink, you want great taste, the right selection, and a reasonable price. Similar thinking can lead you to measure atmosphere in terms of type of music, number of people, and furnishings such as having that checkered red and white table clothe. For location, you might want short distance away, what part of town, and availability of parking or public transit. These measurable requirements are your final branches at the end of the tree.
Given a CTQ Tree for “dinner out”, you can measure your potential choices against those standards and determine the best place to go.
“A Critical to Quality Tree (CTQ Tree) is a way to translate customer needs into measurable requirements.”
Example 2
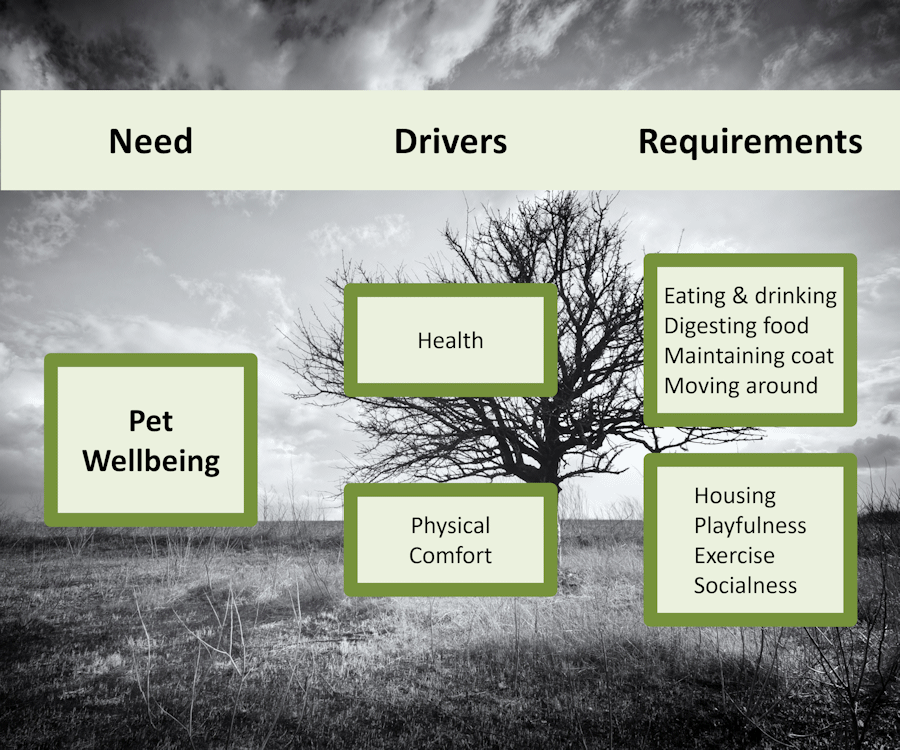
Let’s work another example. In this scenario, “you love animals and have built a small clientele by informally taking care of pets when their owners are away”. How can you turn this into a real business? First off, you need to determine what pet owners would view as needs. This is where VOC comes in. You could survey your current clients, do some competitive analysis, and go through a customer journey map with a few friends that are pet owners. Let’s say you’ve gathered data, analyzed it, and determined that “pet wellbeing” is a critical need. This would go on the left side of your CTQ tree as a need.
Next, ask yourself: What drivers are important considerations for “pet wellbeing”? With input from your VOC studies, you determine Health and Physical Comfort are two critical drivers and should be listed next on the Critical to Quality tree. These two things are your key drivers and would go as the middle branches of the tree.
So, what about pet health that would be informative to share with the pet owner? These become the requirements on the tree. Now, you aren’t a vet, so taking temperature maybe too much, but you could record and report out whether the animal is: eating & drinking well, digesting food normally, maintaining their coat, and moving normally. How about physical comfort – what would be considered standards? Things like house status, playfulness, exercise, and socialness could all be requirements of physical comfort for the animal.
From this analysis, you determine that you could offer an app to clients which gives a rating of all of these requirements at each visit along with a photo. You share this idea with your current clients and every loves it. So, you believe you’ve successfully built out a Critical to Quality tree. Similar analysis could be done for a few other key needs to round out your business plan.
Summary
The process for providing high quality products and services starts with understanding the needs, drivers, and requirements of the customer.
Creating a Critical to Quality Tree is a great way to identify needs, determine drivers, and specify requirements.
When you have your CTQ Tree complete, you are ready to analyze your processes and design improvements which will meet the requirements of your customers.

Lale Lovell
Lale Lovell, Ph.D. is the Vice President of Transformance Advisors. She is a chemical engineer with over 20 years of engineering and management experience in a variety of technology companies in Colorado, including Lexmark and Seagate. Lale brings a wealth of expertise to her role, specializing in Lean thinking and coaching.
Her dedication to continuous improvement and community service underscores her commitment to professional excellence for her clients.
As time permits, Lale likes baking, reading historical fiction, going on walks/hikes, and traveling to new places.
Control Charts
What is Six Sigma?
Three Types of Value
What is SWOT Analysis?
Six Sigma Project Scorecards
Subscribe to our newsletter
References
Critical to Quality by Ted Hessing
3 Types of Customer Needs by Tim Stobierski
Organizational Improvement Acronyms by Transformance Advisors
Organizational Improvement Definitions by Transformance Advisors

